Child Vaccinations
What is a vaccine; It is a biological substance administered to healthy and at-risk individuals (infants, pregnant women, adults and health personnel) in order to protect people from diseases and their bad consequences.
Purpose of Vaccination
- Destroy the infectious agent every time it is encountered.
- Protecting the child against diseases with complications and risk of death.
- Prevent infectious disease outbreaks in the community
- To eradicate deadly diseases from the world.
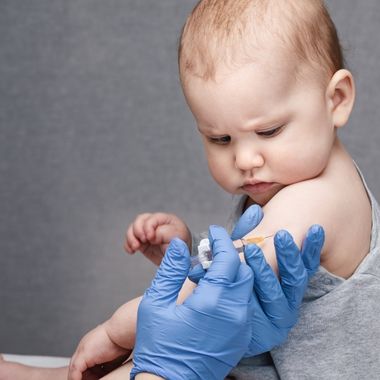



Overview of Vaccine Administration
The vaccination status of every infant, child, adolescent and pregnant woman applying to a health institution should be checked and the missing vaccines should be identified and the opportunity for vaccination should be taken.
Families should be informed about when to come for the next vaccination and the side effects of the vaccine.
A vaccination card should be issued to the baby and the vaccines should be written on the vaccination card with the date.
Vaccine Applications
A separate sterile syringe should be used for each vaccine. Before vaccination, the injection site should be wiped with 70% alcohol and allowed time to dry. A small papule should form at the vaccination site (BCG, PPD). Some vaccines are used directly on the tongue. If vomiting or spitting up occurs within 10 minutes after vaccination, the vaccine should be given again.
BCG (Tuberculosis)
Polio (Polio)
Diphtheria
Whooping cough
Tetanus
Hib (Meningitis)
CPA (Pneumonia)
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
MMR (Measles, Rubella, Mumps)
Chickenpox
Td (Adult tetanus diphtheria)
In the pediatric outpatient clinics of our hospital, vaccines for the prevention of childhood diseases are administered and monitored.
Hepatitis B Vaccination at birth and 1st-6th month:
Turkey is a moderately endemic country in terms of hepatitis B.
In such countries, HBV vaccine is included in the routine vaccination program.
The Ministry of Health recommends it after birth and before discharge.
Hepatitis B vaccine is widely used all over the world. The vaccine has absolutely no chance of causing disease. The vaccine against hepatitis B provides nearly 100% protection.
The 1st dose of hepatitis B vaccine is given immediately after birth. The second dose is given when the baby is 1 month old and the third dose is given when the baby is 6 months old. The vaccine is given through the arm or leg.
In the 2nd month, Tuberculosis Vaccine (BCG), DaPT, (Diphtheria, Acellular Pertussis, Tetanus) iPA (Inactivated Polio-Polio Vaccine), Hib Vaccine (Hemophilus Influenza), Ponomococcus
When your child encounters the germs of these diseases, his or her immune system does not recognize the germs and your child becomes ill. Depending on the type of germ, this illness can be mild, or it can lead to hospitalization, disability or even death.
What is the Bcs vaccine? The purpose of the vaccine is to protect against deadly forms of tuberculosis, especially in young children.
The tuberculosis vaccine (BCG) is administered with a special needle into the skin in the shoulder area when the baby is 2 months old.
The vaccination site should not be touched for the first 3 days and the baby should not be bathed.
Bcg Vaccine Reactions
It does not cause side effects such as fever. Approximately 1-2 months after the vaccination, the vaccination site will first become hard and then red, like a small pimple. This pimple slowly forms a scab and then heals leaving a scar. This wound should not be tampered with and the scab should not be removed.
This is not always the case with vaccination. Sometimes a few months after the vaccination, none of these changes occur. In this case, the vaccine may not have taken. In this case, a test can be done and the vaccine can be repeated if it really did not work.
DaPT, (Diphtheria, acellular pertussis, tetanus), iPAinactivated polio vaccine Hib vaccine
5-pack Mixed vaccine
Mixed vaccine is given to protect against Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Polio and Meningitis.
The newborn baby is given a 5-pack mixed vaccine at the end of the 2nd, 4th, and 6th month. The booster dose is given at the end of the 18th month.
It is applied to the baby's arm or the front part of the leg.
Pneumonia is a febrile, serious lung disease that is particularly severe in children.
The KPA vaccine protects children against this disease.
It is administered at the end of the 2nd, 4th, 6th month and at the age of 1 year.
***Rotavirus vaccine, which is the causative agent of diarrhea, is recommended for children who are not on the 3rd month vaccination schedule of the Ministry of Health.
Rotavirus is the most common cause of severe acute diarrhea in children worldwide and causes high rates of disability and death.
Vaccination is the most important method to control the disease.
Oral 2 doses are administered.***4.month, DaPT, (Diphtheria, acellular pertussis, tetanus) iPA (Inactive Polio-Polio Vaccine), Hib Vaccine (Hemophilus Influenza), Ponomococcus
****5. month rotavirus 2nd dose vaccine
***6.month Hepatitis, Ponomococcus, oral polio
***9.month meningitis vaccine is recommended for children who are not on the Ministry of Health vaccination schedule.
***12.month Pneumococcal, MMR (measles, rubella, mumps), chickenpox
- One in every 100 children who get measles dies.
Measles is more common in winter and spring.
The measles-mumps-rubella-mumps vaccine is given subcutaneously in the arm or leg when the baby is 9 months old and at the age of 1 year.
The chickenpox vaccine was initially designed to prevent the development of chickenpox in children who are likely to have severe disease.
Administered at 12 months (birthday vaccination)
A live vaccine
5 ml SC is applied.
While the vaccine is administered as a single dose under the age of 13, it is administered in two doses with an interval of 6-8 weeks above the age of 13.
Cases where it should be applied in individuals who have not had chickenpox
Over 10 years of age.
Health personnel
Immunosuppressive therapy patients' immediate environment
Candidates for organ transplantation
Chronic skin patients
Those undergoing radiotherapy
Patients who will use salicylates for a long time.
Leukosis in remission
***18.month DaPT, (Diphtheria, acellular pertussis, tetanus) iPA (Inactivated Polio-Polio Vaccine) Hib Vaccine (Hemophilus Influenza), Oral polio, Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is an inflammatory disease of the liver that is transmitted to humans through contaminated water and food contaminated with the hepatitis A virus.
Hepatitis A vaccine is given in 2 doses at the end of the 18th and 24th month.
***24th month Hepatitis A
***DaBT-IPA (Quadrivalent Mixed) and MMR (Measles-Mumps-Rubella-Mumps) vaccines are administered in 1st grade.
***In 8th grade, Td (Tetanus-Diphtheria) vaccine is administered.
When your child encounters the germs of these diseases, his or her immune system does not recognize the germs and your child becomes ill. Depending on the type of germ, this illness can be mild, or it can lead to hospitalization, disability or even death.
Today's modern technology has reduced the likelihood of side effects to almost zero.
Very rarely, some side effects may occur in the body and at the vaccination site after the vaccine is administered.
These include
High fever,
Pain and redness at the vaccination site.
These side effects are usually short-lived, do not require medical treatment and can be easily eliminated by mothers taking simple precautions. Serious side effects are very, very rare but can sometimes occur.
But remember that the risk of getting the disease is much higher than the risk of the vaccine.
Vaccines usually provide 90-99% protection.
If you forget to vaccinate your baby, contact your family doctor immediately and ask for the new vaccination date.
If you get vaccinated elsewhere, inform your family doctor of the vaccination date.

